Lithium-ion battery or lead-acid battery, which is more suitable for
household energy storage systems?
In the past, most residential users who deployed solar energy storage
systems used lead-acid batteries, especially batteries that were completely off
the grid, but now residential energy storage systems increasingly use lithium
batteries. So, which one is more suitable for energy storage systems?
Lithium-ion batteries or lead-acid batteries? The following is an overview of
the pros and cons of both.

(1) Application of lead-acid batteries
Since the 1970s, lead-acid batteries have been used as a backup power
source for residential solar power generation facilities. Although similar to
traditional car batteries, they are called Deep Cycle batteries.
Traditionally, the direct cost of lead-acid batteries is lower than that of
lithium-ion batteries, which makes them more attractive to residential users.
However, their cycle life is much shorter than that of lithium-ion batteries.
Therefore, in the long run, the cost of lithium-ion batteries will be lower.

The number of charge and discharge times of lead-acid batteries is
generally 500 times, while that of lithium-ion batteries is between 1000 and
4000 times. The working life of lead-acid batteries is much lower than that of
lithium-ion batteries.
The actual service life of most lead-acid batteries is about 1-2 years, and
there is a corresponding warranty period. Therefore, in the overall use of solar
power generation facilities, residential users will have to replace lead-acid
batteries multiple times.
The energy storage efficiency of lead-acid batteries is lower than that of
lithium-ion batteries, and they cannot be charged or discharged as quickly as
lithium battery energy storage systems. A study by the US National Renewable
Energy Laboratory (NREL) found that when a lead-acid battery releases 80% of its
capacity, it can only withstand 600 cycles of charging and discharging, and its
capacity will then decrease significantly.
Because lead-acid batteries have relatively low energy storage efficiency
and cannot be completely discharged, lead-acid batteries require more energy
storage capacity and space than lithium-ion batteries. Lead-acid batteries are
also much heavier than lithium-ion batteries. Lead-acid batteries require a
stronger support and require more space than lithium-ion battery packs.
Lead is a toxic heavy metal. Although it is recyclable, it can still cause
pollution due to improper handling.
(2) Application of lithium ion battery
Lithium-ion batteries are rapidly becoming the first choice for many power
applications, and more and more residential solar power generation facilities
use lithium-ion battery energy storage systems. However, the most important
aspect of lithium-ion batteries is their high short-term cost.
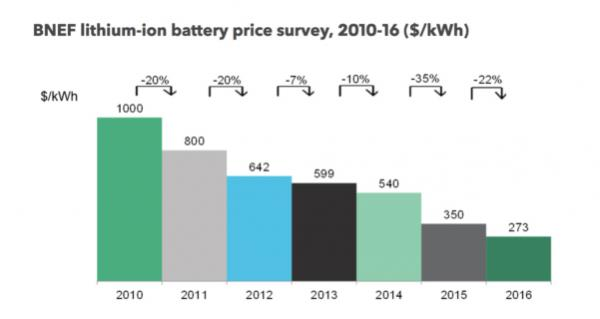
The cost of lithium-ion batteries is falling rapidly. In the past few
years, Lazard's latest survey report in November 2017 pointed out that the
installation cost of lead-acid battery energy storage systems for residential
solar energy ranged from US$598 to US$635 per kWh. The installation cost of
lithium-ion batteries ranges from US$831 to US$1,089 per kWh.
But the low price of lead-acid batteries hides many other costs, such as
shorter service life and higher operating costs. Over time, the cost of each
kind of battery system will be very different. Lazard's survey shows that the
cost per MWh of energy storage systems using lithium-ion batteries is lower than
that of lead-acid batteries.
The cost of lithium batteries has dropped to a certain extent every year,
while the cost of lead-acid batteries has not much room for reduction due to raw
material and environmental issues.
For these reasons, it will be very important to understand the true
application cost of lithium-ion batteries and lead-acid batteries currently used
in residential energy storage systems.
In terms of working life, it is expected that lithium-ion batteries will
continue to operate for about 5 years, and they can maintain a stable level of
charge and discharge without significantly reducing the capacity.
Lithium-ion batteries can also be charged quickly. Lead-acid batteries can
be fully charged in up to 16 hours, but even the slowest-charging lithium-ion
batteries can be fully charged in about only 4 hours.
In terms of weight, lithium-ion batteries used in residential energy
storage systems are not light, but they are much lighter than lead-acid
batteries. The 13.5 kWh Tesla Powerwall weighs about 278 pounds, the 1.7 kWh
lead-acid battery weighs about 132 pounds, and the lead-acid battery with the
same capacity as the Powerwall will weigh more than 1,000 pounds!
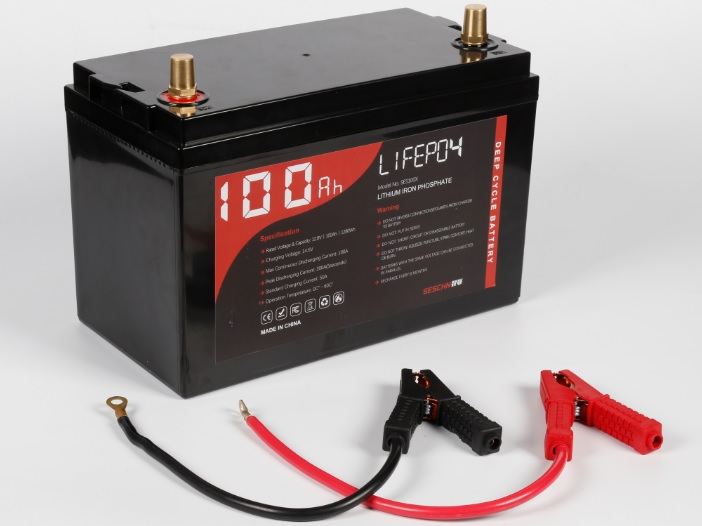

In addition, lithium-ion batteries do not have the environmental protection
problems of lead-acid batteries.