27.8GW components! Restrictions on imports from China failed to slow down
U.S. solar imports
A research report by Rystad Energy shows that the United States has failed
to reduce its dependence on solar imports, especially by adopting measures to
restrict imports from China.
According to the report, in 2021, the United States is expected to import a
record 27.8GW of solar photovoltaic modules from a series of countries, which is
higher than last year's 26.7GW.
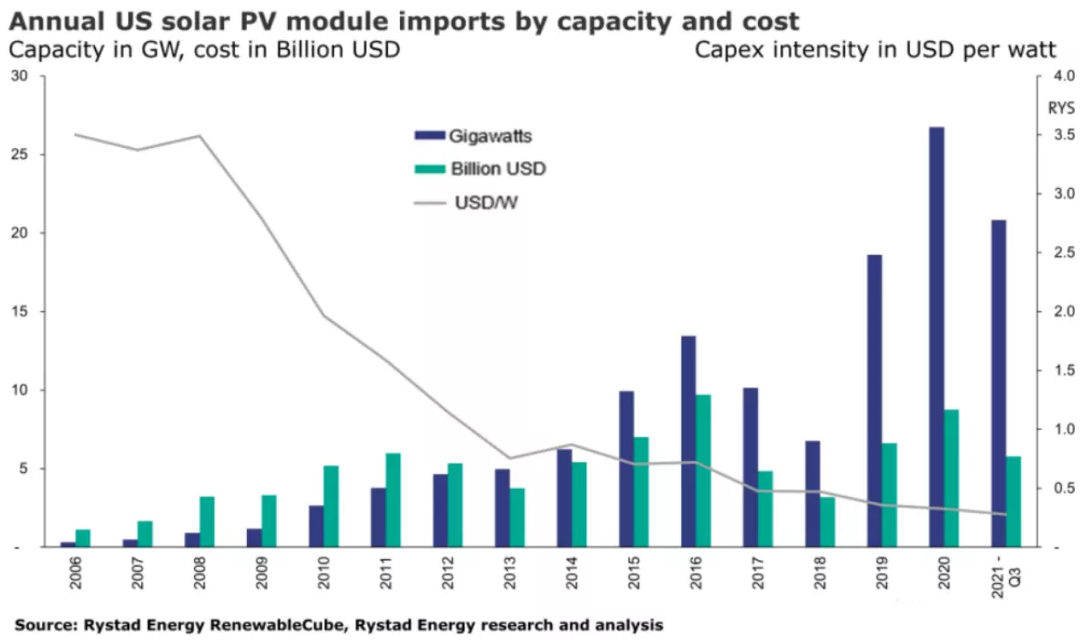
If the recent import trend continues, total solar photovoltaic imports in
2021 will reach 8.9 billion U.S. dollars, a slight increase from 2020's 8.7
billion U.S. dollars. It is worth noting that 8.7 billion U.S. dollars is also a
new record at the time.
In this regard, the importance of China in the dominance of the United
States and most global markets has been fully proven, thanks to the efficiency
and cost reduction, subsidies, and low sales margins for Chinese
manufacturers.
In 2008, 22% of all photovoltaic modules imported into the United States
came from China. In 2011, the share of photovoltaic products imported from China
has risen to 57%.
Although tariffs have reduced imports from China, the demand is met by
other sources, not the domestic manufacturing of the United States. In 2021, the
total amount of solar photovoltaic modules manufactured in the United States is
expected to be 5.2GW, of which about half will come from thin-film modules,
which are mainly manufactured by First Solar. The other half is silicon-based
modules with a wider range of use. The estimated 2.5GW capacity accounts for
only 50% of the total US capacity.
The real threat to Chinese manufacturing is Malaysia, which will become the
market leader in 2020, occupying 42% of the US import market share, followed by
Vietnam with 38%. Since 2021, these countries accounted for 31% and 28.8%
respectively, and Thailand ranked third with 26.2%.
It is worth noting that many new imported products from Southeast Asia also
come from factories owned by China. The decline in market share in Malaysia and
Vietnam indicates an increase in imports from other countries, including
Thailand, South Korea and even India. Since 2021, only 1% of imports come from
regions outside of Asia. So far, actions against major Southeast Asian countries
have been shelved.
In 2018, the Trump administration doubled its efforts to promote the
domestic solar photovoltaic module manufacturing supply chain in the United
States, imposing Section 201 tariffs on imported c-Si products. This policy
severely affected the PV imports and installed capacity in 2018, reducing the
import volume of modules to 6.8GW, a decrease of 66.7% from 10.2GW in 2017.
However, due in part to temporary tariff exemptions and scheduled tariff
cuts, the industry rebounded in 2019 and 2020.
The annual production capacity of photovoltaic modules in the United States
is 5.5GW. Nevertheless, this production capacity is entirely composed of
modules, and the battery part is completely dependent on overseas. Asia is the
leader in the solar cell market. As of now, 52% of imported solar cells in the
United States come from South Korea, 25% from Malaysia, and 15% from Thailand.
The United States will set a record for imported photovoltaic cells in 2021, and
is expected to reach 3GW by the end of this year, surpassing the 2.5GW in
2019.
This shows that although the domestic module production capacity in the
United States is rising, the current import level shows that the capacity
utilization rate is only 50.8% without considering the domestic photovoltaic
cell production.

Lithium-ion battery (LIB) has become the main energy storage solution in
modern social life. Among them, lithium iron phosphate batteries are a perfect
replacement for lead-acid batteries, and they are the first choice for
grid-connected peak shaving, off-grid energy storage, photovoltaic energy
storage, UPS, data center and other industries.
Solar power generation system with lithium battery energy storage system is
a very promising clean energy.




































