Lithium-ion battery thermal stability and safety analysis of overcharge,
high temperature and short circuit
In recent years, reports of fires and even explosions caused by lithium-ion
batteries are not uncommon.
Lithium-ion batteries have strong dangers, especially in the case of abuse,
safety issues are more prominent.
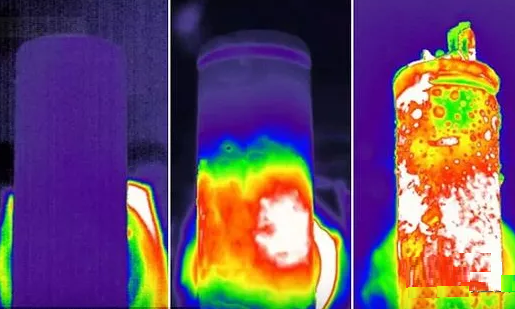
1. Thermal stability analysis of lithium-ion battery materials
The fire hazard of lithium-ion batteries is mainly determined by the amount
of heat generated by chemical reactions in various parts of the battery. In the
final analysis, the fire hazard of lithium-ion batteries depends on the thermal
stability of the battery material, and the thermal stability of the battery
material depends on the chemical reactions that occur between its internal
parts.
1) Influencing factors of the thermal stability of anode materials
The onset temperature of the negative electrode material's heat generation
increases with the increase of the particle size.
2) Factors affecting the thermal stability of cathode materials
The initial temperature of the reaction between the positive electrode
material and the electrolyte increases as the stoichiometric number
decreases.
The higher the content of Ni in the cathode material, the more unstable it
is, and the higher the content of Mn, the more stable it is.
3) Influencing factors of electrolyte thermal stability
The organic solvent DMC is an important factor causing the instability of
the electrolyte, and the higher the DMC content, the more unstable the
electrolyte.
The electrolyte can make the positive electrode react at a lower
temperature, and different solvents and lithium salts in the electrolyte are
suitable for different positive electrode materials.
2. Safety analysis of lithium-ion battery abuse
The safety of lithium-ion batteries mainly depends on the thermal stability
of battery materials, and is also closely related to abuse conditions such as
battery overcharge, needle stick, extrusion, and high temperature.
1) Overcharge
The overcharge test simulates the potential safety hazards of the battery
when there is an error in the charger voltage detection, the charger fails or
the wrong charger is used.
The thermal runaway caused by overcharging may come from two aspects: on
the one hand, the Joule heat generated by the current, and on the other hand,
the reaction heat generated by the side reactions of the positive and negative
electrodes. When the battery is overcharged, the negative electrode voltage
gradually increases, and the process of delithiation becomes more and more
difficult. This causes the internal resistance of the battery to increase
sharply, and therefore generates a large amount of Joule heat, which is more
obvious when charging at a high rate. The positive electrode oxidant in the
overcharged state releases a lot of heat, and the negative electrode also reacts
exothermically with the electrolyte. When the rate of heat release is greater
than the rate of heat dissipation of the battery, and the temperature rises to a
certain level, thermal runaway will occur.
2) High temperature
The simulated environment high temperature test can be carried out by using
the hot box test. The hot box test simulates the improper use of the battery at
a high temperature, such as placing a mobile phone in an exposed car, or putting
a mobile phone or electronic product in a microwave oven, and the temperature
can reach 130°C or even 150°C. In the case of thermal abuse, the heat source is
not only from the positive and negative electrode materials inside the battery
and its reaction with the electrolyte, the separator film melts and shrinks at
high temperatures, resulting in a short circuit between the positive and
negative electrodes. The Joule heat generated by the short circuit is also an
important heat source during the hot box test. .
3) Short circuit
The short circuit of the battery is divided into external short circuit and
internal short circuit.
External short circuit generally refers to the short circuit caused by the
direct contact between the positive and negative electrodes; internal short
circuit refers to the short circuit in the area where the battery is affected by
foreign objects when the battery is punctured by a sharp object or is impacted
or squeezed.
The safety research of internal short circuit generally adopts methods such
as acupuncture, extrusion, etc. The purpose is to simulate the situation of the
battery being punctured, collided, and squeezed by foreign objects. Acupuncture
causes a short circuit of the battery at the acupuncture point. The
short-circuit area forms a local hot zone due to a large amount of Joule heat.
When the temperature of the hot zone exceeds the critical point, it will cause
thermal runaway, causing smoke, fire or even explosion hazards. Extrusion is
similar to acupuncture, both of which cause local internal short circuits and
may cause thermal runaway. The difference is that squeezing does not necessarily
cause damage to the battery casing. If the casing is not damaged, it means that
flammable electrolyte will not leak from the hot zone, and the heat dissipation
effect from the hot zone is worse.
It is often much more difficult to test the local internal short circuit of
the battery caused by squeezing and needle sticking than the external short
circuit test. This is because the internal heat of the battery tends to be
uniform when the battery is externally short-circuited, and the Joule heat
generated by the external short-circuit battery will not Directly trigger the
thermal runaway reaction of the battery.

Lithium-ion battery (LIB) has become the main energy storage solution in
modern social life. Among them, lithium iron phosphate battery is a perfect
replacement for lead-acid batteries, and it is the first choice for
grid-connected peak shaving, off-grid energy storage, photovoltaic energy
storage, UPS, data center and other industries.




































