Although many UPS manufacturers have begun to gradually replace lead-acid
batteries with lithium-ion batteries in recent years, generally speaking, the
progress is relatively slow. According to relevant industry data, more than 90%
of the newly added UPS systems still use lead-acid batteries. As a senior
lithium battery service provider, many of our customers are in the UPS industry,
and we have a deep understanding of this.

First, let's briefly explain a few concepts.
What is UPS: The full name is Uninterruptible Power System/Uninterruptible
Power Supply. It is composed of a battery, an inverter that converts direct
current into alternating current, a control module, a monitoring module, a
charging module and other circuits.
The use of UPS: to supply a stable and uninterrupted power supply to a
single computer, computer network system or other power electronic equipment.
When the mains input is normal, the UPS will stabilize the mains and supply it
to the load. At this time, the purpose of the UPS is an AC voltage stabilizer,
and it also charges the battery inside the machine. When a power outage occurs
in the power grid, the UPS can immediately supply qualified AC power to the load
by switching the energy stored in the battery to the load through the method of
inverter switching, so as to keep the load in a normal working state and protect
the software and hardware of the load. damaged.
Lithium-ion battery: a battery that uses lithium metal or lithium alloy as
the negative electrode material and uses a non-aqueous electrolyte. There should
be two types of lithium-ion batteries in UPS: ternary lithium-ion batteries and
lithium iron phosphate batteries. The lithium iron phosphate battery is very
safe and the price is very suitable. It is the variety used by the mainstream
UPS.
Lead-acid battery: A battery in which the electrodes are made of lead and
its oxides, and the electrolyte is a sulfuric acid solution. Lead-acid batteries
have relatively high safety performance, but the energy-to-volume ratio is too
low, resulting in cumbersomeness, large footprint, short lifespan, and short
maintenance cycle.
Accept, SES Power will analyze the reasons why UPS manufacturers are not
very accepting of lithium-ion batteries for you:
1. Initial cost
In fact, the influence of this factor has been gradually reduced, and even
more conducive to lithium-ion batteries. Because with the rapid development of
electric vehicles and large lithium battery energy storage systems, the scale
effect of lithium ion batteries has emerged, especially lithium iron phosphate
batteries.
2. Differences in lithium battery cells
Large-scale UPS has very high power, so the busbar voltage is very high.
For example, the busbar rated voltage of mainstream UPS often used in data
centers is 384V, then 192 2V single lead-acid batteries will be used. is very
large. Switching to the lithium iron phosphate platform will require nearly 120
lithium iron phosphate batteries, which means that many cells need to be used in
series and parallel, and the individual performance differences of lithium
batteries will cause the performance and safety of the entire battery pack to
decline. .
3. UPS manufacturers need to adjust parameters
Because the UPS judges the battery capacity according to the bus voltage,
and the discharge curves of lithium batteries and lead-acid batteries are quite
different, UPS manufacturers need to adjust the corresponding parameters. Of
course, this adjustment is relatively simple.
4. Charging mode
The charging circuit of the traditional UPS using lead-acid batteries is
very simple and inexpensive: the charging voltage accuracy is not required, and
control such as disconnection is not considered. Lead-acid batteries can remain
fully charged for a long time but their lifespan is not greatly affected.
Lithium batteries need a precise and stable charging voltage, and they need to
stop charging after being fully charged: because long-term floating charging
will lead to lithium precipitation inside the cell, which will eventually lead
to damage or even failure of the cell.
Therefore, if the UPS manufacturer changes from the configuration of
lead-acid batteries to lithium batteries, then the circuit of the battery must
be completely changed, and the higher-end ones need to read the parameters of
the lithium battery for optimal settings. This is an event that increases both
cost and probability of failure for many UPS manufacturers.
5. Power
UPS requires a large amount of current. Because lead-acid batteries do not
have BMS or PCM configuration, they only need to consider factors such as
battery parameters and wires. Lithium battery testing needs to consider the
bearing capacity of the BMS, as well as the impact of switching, which will
increase costs and increase risks.
For many of the above reasons, you will find that in addition to the price
factor, it is completely a matter of the will of UPS manufacturers. SES Power
believes that the main reason is that the UPS market is relatively mature, and
the replacement of lead-acid batteries by lithium batteries is not an iterative
product in this industry. It can only be a matter of upgrading accessories.
Moreover, in the UPS stock market, price is indeed the core and most critical
factor. The technical advantages of lithium batteries over lead-acid batteries
are not considered "advantages" in some UPS application scenarios, and users
will naturally prefer cheaper options. , Mature lead-acid batteries. Therefore,
UPS manufacturers will only consider using lithium batteries in occasions with
extremely high space requirements.
However, in recent years, the situation has changed a lot, because end
users have begun to require UPS manufacturers to use lithium iron phosphate
batteries, which means that the use of lithium batteries in UPS in recent years
is more of a push from the user side. SES Power has many years of rich
experience in the fields of energy storage and UPS. Many of our customers buy
our products, such as 48V100Ah, for use in the UPS field. There are also
customers who have customized high-voltage lithium iron phosphate battery packs
for us, such as 384V50Ah, which are also used in medium and large UPS.
Why did this happen? SES Power summarizes it for the following reasons:
1. The initial price is not the final cost
The initial cost of lead-acid batteries is indeed lower than that of
lithium iron phosphate batteries, but in practical applications, the average use
time of lead-acid batteries is only one to two years, while lithium iron
phosphate batteries can be used for a minimum of more than 5 years. In addition
to the cost of replacement, there is also the risk of downtime and labor for
replacement. Therefore, if the cost is calculated on an annual basis, there is
essentially no difference between the two, and even lithium batteries have an
advantage.
Let's take lithium iron phosphate batteries, which can perfectly replace
lead-acid batteries, as an example. In 2017, the price of lithium iron phosphate
battery was about US$0.22/wh. In 2022, despite the influence of international
commodities and inflation, the price will still drop to US$0.14/wh. The price of
lead-acid batteries has barely changed over the five years and remains around
$0.07/wh. But we must make it clear that lithium iron phosphate can achieve a
cycle life of 4000 weeks, while lead-acid batteries only have a cycle life of
500 weeks. From the perspective of long-term use cost, lithium iron phosphate
batteries have more advantages.
2. Intelligence is an inevitable trend
Lead-acid batteries do not need BMS for protection functions such as
overcurrent and overcharge. Lithium-ion batteries must have BMS for accurate
monitoring and protection throughout the process. This is a double-edged sword.
Although lead-acid batteries save the cost of BMS, it also makes the digital
monitoring of lead-acid batteries impossible for the system. Lithium-ion
batteries can be digitally monitored and accurately measured through BMS, such
as RS485 or CAN communication with the system to report the voltage, capacity,
temperature and other status of the battery to the system.
Although lithium batteries must be equipped with BMS, which increases costs
and risks, it brings more benefits to end customers: accurate data and
intelligent control. Lead-acid batteries can't do this at all. The larger the
UPS is, the more it pursues the requirements of the Internet of Things. At this
point, the end user has far more say than the UPS manufacturer.
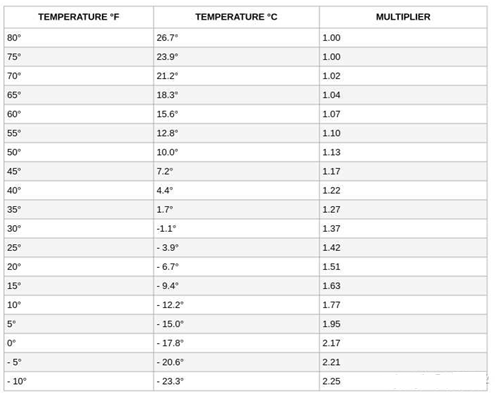
3. Temperature is a factor
The normal operating temperature range of the lithium-ion battery is
-20-60°C, which does not require an air-conditioning system to control the
temperature, reducing equipment installation costs, maintenance costs and
electricity costs. The normal operating temperature range of lead-acid batteries
is 10-35°C. Too low temperature will seriously reduce the power, capacity and
other parameters of lead-acid batteries, so certain temperature control is
required.
And there is another important factor, the life of the lead-acid battery
will be closely related to the ambient temperature of the working state. Many
batteries perform well in the right temperature range; however, when extreme
temperatures occur, you need a reliable battery that follows well-established
best charging and storage practices to maintain battery performance. The extreme
heat accelerates chemical reactions inside the battery, leading to increased
self-discharge and plate corrosion, possibly leading to sulfation.
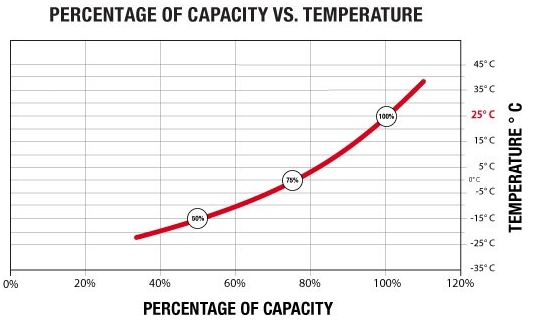
For every 5.55 degrees Celsius increase in ambient temperature, the life of
sealed lead-acid batteries is cut in half. A stationary lead acid battery should
last 4 years at normal temperatures, only 2 years if exposed to 34 degrees
Celsius, or even less if exposed to typical desert temperatures of 41 degrees
Celsius.
4. The rapid development of lithium batteries
With the rapid development of electric vehicles and large-scale lithium
battery energy storage systems, while the cost of square aluminum-shell lithium
iron phosphate cells has dropped rapidly, the single-cell capacity of the cells
has reached 100Ah, 150Ah, 200Ah or even 300Ah, such as SES Power 12V100Ah,
12V200Ah, 24V100Ah, 24V200Ah, 36V100Ah, 48V50Ah, 48V100Ah and other lead-acid
replacements, wall-mounted home energy storage, mobile home energy storage,
12V30Ah, 12V50Ah, 12V60Ah car starter batteries with high-performance rate
lithium batteries (maximum The peak current can reach 1500A) lithium iron
phosphate battery series, almost all square aluminum shell lithium batteries
from famous manufacturers such as CATL, EVE, BYD are used.
5. Environmentally friendly
Lithium-ion batteries, especially lithium iron phosphate batteries, do not
contain any heavy metal elements that are harmful to the human body. Lead-acid
batteries contain lead, antimony and other heavy metals, which are prone to
leakage during use, maintenance, and disposal. When the internal sulfuric acid
overflows, it is easy to cause equipment corrosion and personal injury
accidents.
6. Discharge stability
The same fully charged lithium-ion battery and lead-acid battery, at the
same temperature, use different rates of discharge current, the discharge output
characteristics of lithium-ion batteries are very stable, while the discharge
output characteristics of lead-acid batteries are very different, which will
cause Power is unstable.
Finally, SES Power summarizes for you: There are generally two types of
UPS. Low-power ones use low-voltage battery packs, boost inverters, and
large-capacity ones use many batteries in series to directly invert the phase
voltage of the mains. Low-power UPS is mainly used in small computer room
offices and homes, and there are no full-time maintenance personnel, so in this
market segment, the trend of lead-acid batteries being replaced by lithium
batteries is obvious. High-power UPS is mainly used in data centers, and the
initial cost is very concerned. It is usually easier to use lead-acid batteries
to achieve the purpose of winning the project, so lead-acid batteries are still
the mainstream.
The fastest growing occasion for lithium batteries is the 48V DC power
supply in communication base station equipment, home energy storage and other
scenarios. In terms of technical route, UPS was used on a large scale at home
and abroad, especially abroad, before 2000. At that time, the price of lithium
batteries was very high, so the batteries used by UPS at the beginning were
lead-acid batteries. With the development and maturity of lithium batteries,
even high-power UPSs are gradually replaced by lithium batteries, especially in
places with high volume requirements. It is expected that in the near future,
lithium batteries will accelerate to replace lead-acid batteries. Be the first
choice for UPS products.





































